Link: https://leetcode.com/problems/binary-tree-vertical-order-traversal/
Solution:
Intuition
This is a very nice problem that recruits a nice property of binary trees. The left child of the parent is shifted one column to the left and the right child is shifted one column to the right. We can use this property to determine the vertical column of every node.
For example
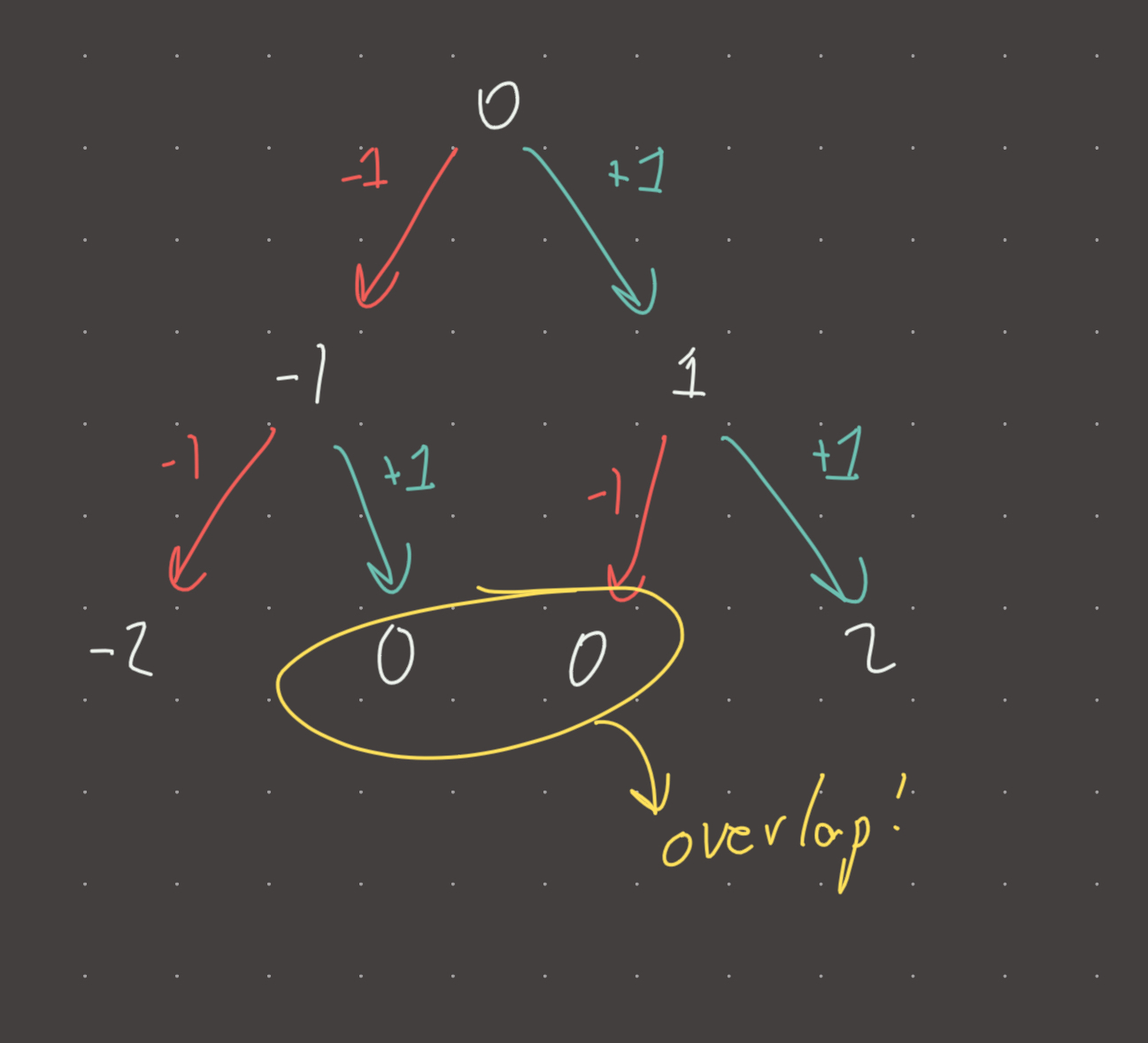
0 start at 0 column for the root
-1 1 0-1, 0+1 for leftchild/right child columns
-2 0 0 2 ...and so on
If we start at column zero for the root node like in the above example, the leftmost columns will be the most negative. We can’t really use a 2d-array here to insert node values because we don’t know in advance how wide the tree is. We could of course traverse twice to normalize the width, but this is wasteful. DFS or BFS is suitable for traversal (choose BFS for efficiency)
A more elegant solution is to store node values in a hashmap with the key being both negative and positive columns. After all nodes are stored, we can convert the hashmap into a 2d array and sort by the key. Then just slice out the key and return the result.
Implementation
def vertical_order(root):
cols = {}
queue = deque([(root, 0)])
while queue:
node, col = queue.popleft()
if node is None:
continue
if col not in cols:
cols[col] = []
cols[col].append(node.val)
queue.append((node.left, col-1))
queue.append((node.right, col+1))
cols = [(col, nodes) for col, nodes in cols.items()]
cols.sort()
return [nodes for _, nodes in cols]
#time: o(nlogn)
#memory: o(n)Visual
Review 1
I pretty much instantly knew how to solve this but initially tried with a DFS algorithm. Unfortunately DFS yields the improper order. DFS is not impossible but the solution is contrived. BFS is the natural algorithm here because of the left-to-right traversal (its even in the problem statement). Why is this the case?
1
/
2
/ \
4 5
\
6
\
7
We can see in the above tree that the result should be:
[[4], [2,6], [1,5,7]]
Lets look at the last column [1, 5, 7]. Is this the ordering we get in a DFS traversal? NO!
DFS seeks the leftmost node, so actually we would get [1, 7, 5]. The colunm is correct but the ordering is not.
For DFS to work, each node must be a tuple with it's row, and then we sort... or just use BFS.