Link: https://leetcode.com/problems/find-in-mountain-array
Solution:
Topics: binary search
Intuition
This is a great problem requiring some creative usage of binary search. The key to solving this problem is understanding that everything to the left of the peak (largest number in the mountain array) is sorted is ascending order, and everything to the right of the peak is sorted is descending order.
Since the target could be on either side of the peak, if we knew where the peak was, we could search the left side and the right side independently. The partitions would have to be searched independently because searching an increasing array is different from searching a decreasing one.
So the main problem here is finding the index of the peak to delineate the left and right partitions. If we look closely thought, we can use binary search to find the peak itself! How? Its very simple:
mountain_arr = [1,2,3,4,3,2,1]
we can see that the peak is 4 at index 3, but what makes it the peak?
for all peaks, the following is true: arr[i-1] < arr[i] > arr[i+1]
or in otherwords, the peak must be larger than its adjecent numbers.
Bulding on this, we can also determine if any number is in the left partition or the right partition:
for all numbers in left: arr[i-1] <= arr[i] <= arr[i+1]
for all numbers in right: arr[i-1] >= arr[i] >= arr[i+1]
Now that we understand what makes a peak number, a left number, and a right number, we can perform binary search to find the peak!
If the number is a left number, the peak must be further to the right. If the number is a right number, the peak must be further to the left!
Implementation
def find_in_mountain(target, mountain_arr):
arr_len = mountain_arr.length()
peak = None
l = 0
r = arr_len - 1
while l <= r:
mid = (l + r) // 2
mid_num = mountain_arr.get(mid)
r_num = mountain_arr.get(mid + 1) if mid != arr_len-1 else float('-inf')
l_num = mountain_arr.get(mid - 1) if mid != 0 else float('-inf')
if mid_num > l_num and mid_num > r_num:
peak = mid
break
elif mid_num <= r_num:
l = mid + 1
else:
r = mid - 1
l = 0
r = peak
while l <= r:
mid = (l + r) // 2
num = mountain_arr.get(mid)
if num == target:
return mid
elif num < target:
l = mid + 1
else:
r = mid - 1
l = peak
r = arr_len - 1
while l <= r:
mid = (l + r) // 2
num = mountain_arr.get(mid)
if num == target:
return mid
elif num < target:
r = mid - 1
else:
l = mid + 1
return -1
#time: o(logn)
#memory: o(1)Mnemonic
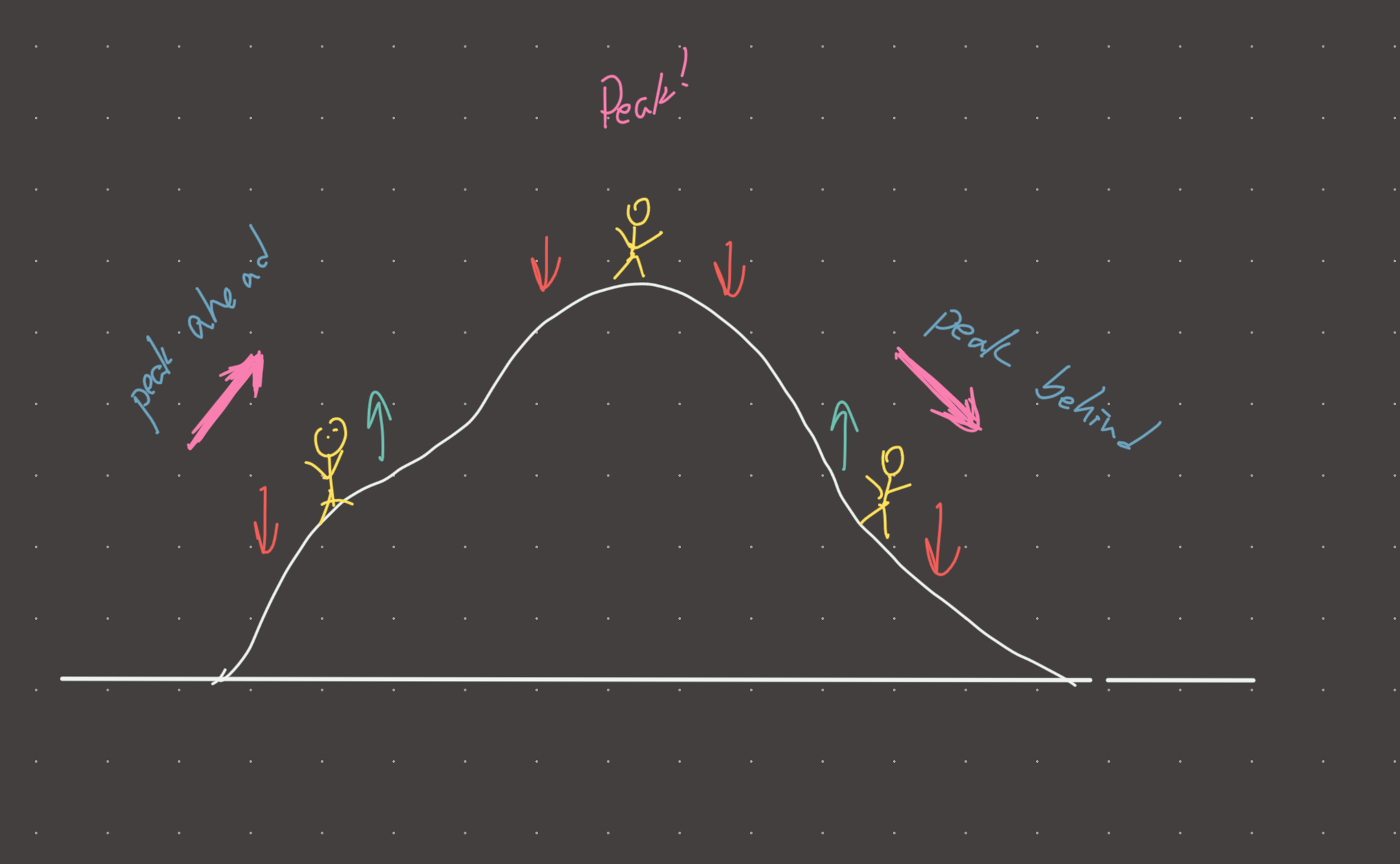
You are climbing a mountain. You look begin you, the terrain is lower. You look in front of you, the terrain is higher. You reach the top. You look left, the terrain is lower. You look right, the terrain is higher. You descend the mountain. In front of you the terrain is lower and behind you the terrain is higher.
Visual