Link: https://leetcode.com/problems/linked-list-in-binary-tree/
Solution:
Topics: tree, linked list, DFS
Intuition
This is a pretty easy problem but sadly I struggled with it because I was committed to solving it with a single DFS function and nothing more. This led to branch factor explosion, and a myriad of edge cases. I made it work, but it was ugly.
It then occurred to me (duh) that we can simply find all potential starting points and then simply verify if they lead to the list being exhausted. This does require two functions but it is a far more logical and simple approach to the problem.
Implementation
def list_in_tree(root, head):
starts = []
def find_starts(node):
if node is None:
return
if node.val == head.val:
starts.append(node)
find_starts(node.left)
find_starts(node.right)
def verify(tree_node, list_node):
if list_node == None:
return True
if tree_node == None:
return False
if tree_node.val != list_node.val:
return False
left = verify(tree_node.left, list_node.next)
right = verify(tree_node.right, list_node.right)
return left or right
find_starts(root)
for tree_node in starts:
if verify(tree_node, head):
return True
return False
#time: o(n**m)
#memory: o(n)Visual
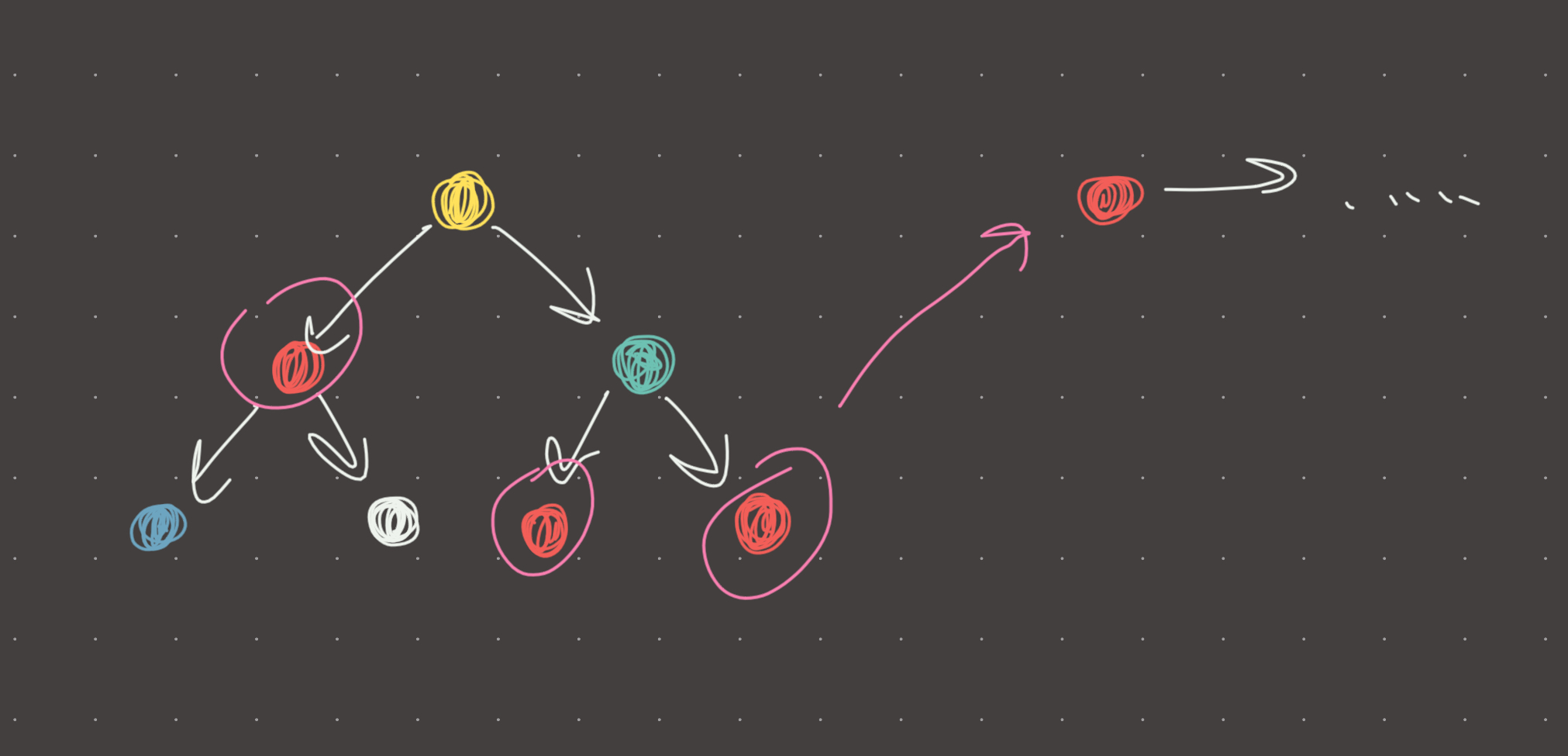
Review 1
Crushed this one.