Link: https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-number-of-events-that-can-be-attended/
Solution:
Topics: heap, sorted order, greedy, simulation
Intuition
Extremely tricky problem. The key insight is that we must iterate over all possible days, because conceivably we can attend a different event on each day. Choosing which event is the tricky part. Basically, if an event starts on a particular day, we add it’s end day to a min_heap because we want to prioritize events that end sooner, since there is less opportunity to attend them.
We must sort events by start day and then iterate over days, all the while moving a pointer for events when a start day is reached.
Implementation
def max_attended(events):
days = max([end for start, end in events])
events.sort()
res = 0
i = 0
min_heap = []
for day in range(events[0][0], days+1):
while min_heap and min_heap[0] < day:
heappop(min_heap)
while i < events[i][0] == day:
heappush(min_heap, events[i][1])
i += 1
if min_heap:
heappop(min_heap)
res += 1
return res
#time: o(nlogn)
#memory: o(n)Visual
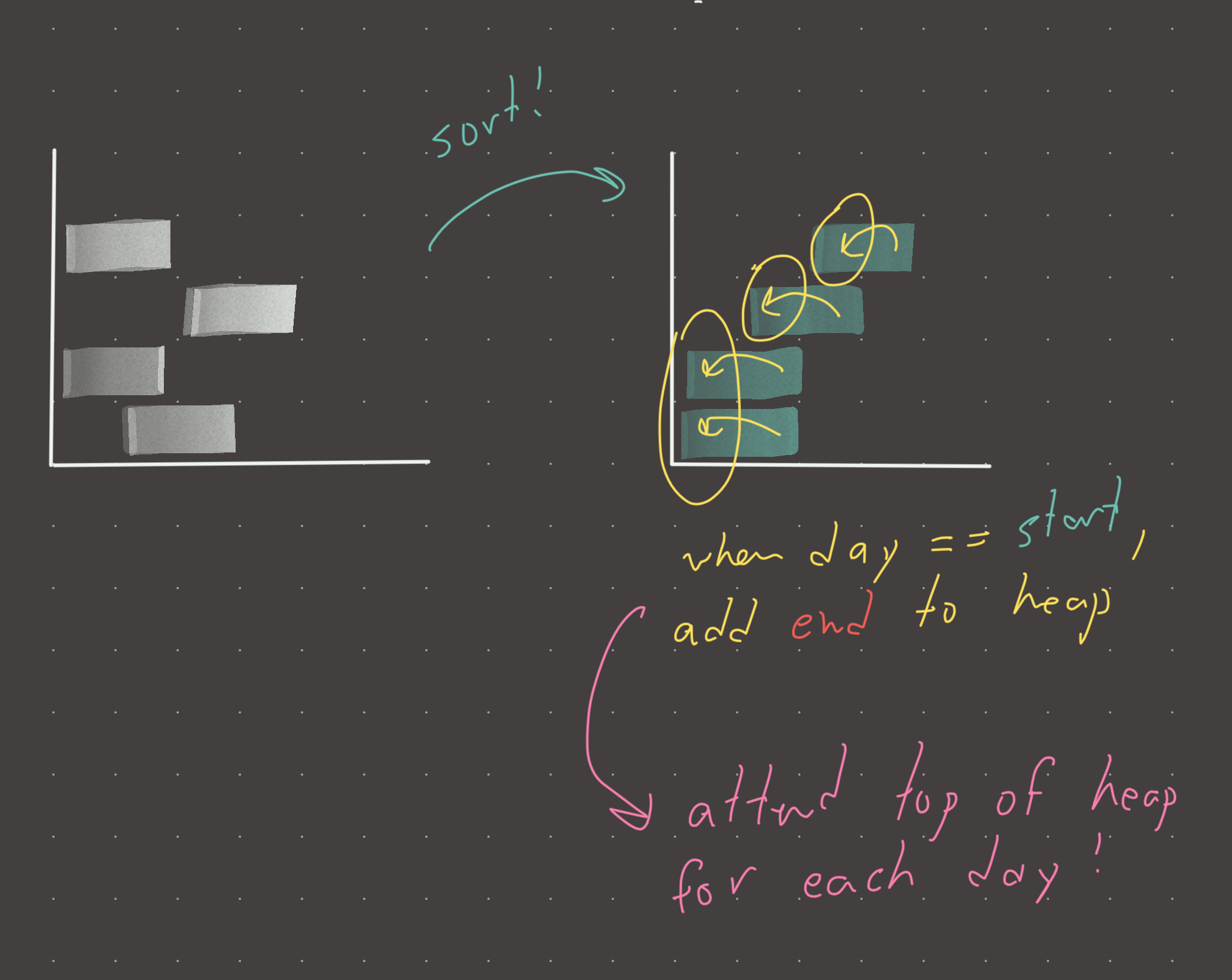
Review 1
Got stumped by this one again. The difficulty comes from the fact that you don’t have to attend the entirety of the event.
Basically we sort the events by start day and iterate through all possible days. Add the end day of all events that start on the current day to a min_heap. This creates a “pool” of events in that can be attended at the current moment. The top of this min heap is the event that is ending the soonest! We want to attend that event because we may not have an opportunity to do so in the future!
Be sure to “clean” the min heap from events that have already ended (these can no longer be attended).
If after cleaning and adding, the heap is not empty, attend (pop) the top of the heap and increment the result.
Here is a demonstrative example:
events = [[1,5],[1,5],[1,5],[2,3],[2,3]]
----- 1, 5
----- 1, 5
----- 1, 5
-- 2, 3
-- 2, 3
day 1
------------
heap = []
[1, 5],[1, 5],[1, 5] ---> add ends to heap
heap = [5, 5, 5]
^ attend this event and pop it
day 2
------------
heap = [5, 5]
[2, 3], [2, 3] ---> add ends to heap
heap = [3, 3, 5, 5]
^ attend this event and pop it
day 3
------------
heap = [3, 5, 5]
[] ---> no events start on day 3
heap = [3, 5, 5]
^ attend this event and pop it
day 4
------------
heap = [5, 5]
[] ---> no events start on day 4
heap = [5, 5]
^ attend this event and pop it
day 5
------------
heap = [5]
[] ---> no events start on day 5
heap = [5]
^ attend this event and pop it
5 events can be attended!
So essentially, sorting the events tells us when they can be started and the min_heap tells us when they are ending. We choose the ones that end the soonest (top of the heap).
Review 2
Solved this one pretty easily.