Link: https://leetcode.com/problems/poor-pigs/
Solution:
Intuition
Really weird problem, but the iterative approach kind of makes sense. I will improve this editorial upon future revisions.
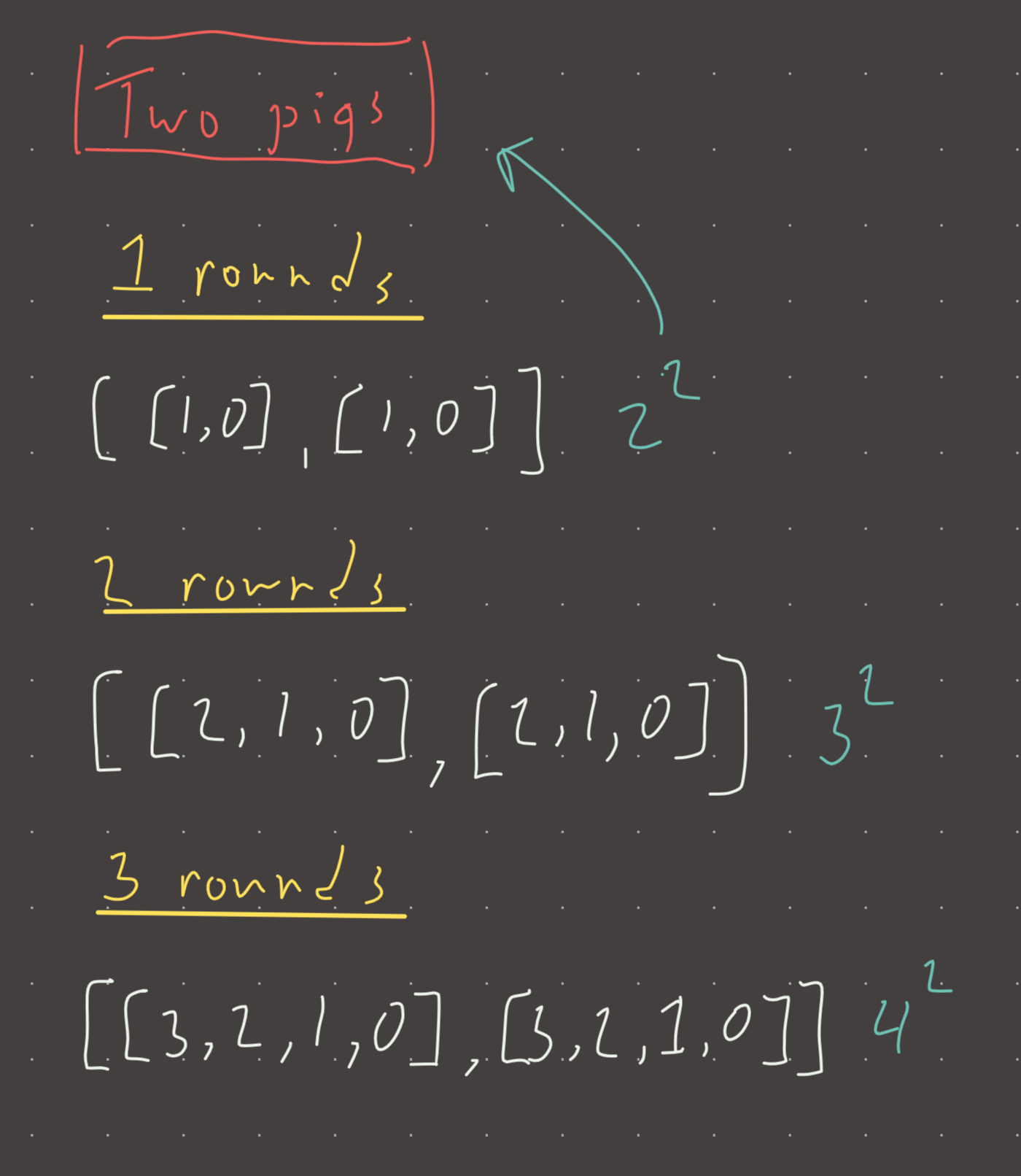
The key insight seems to be the fact that in one round of testing, n pigs can test 2**n buckets. In two rounds of testing, n pigs can test 3**n buckets. Or more generally, (rounds+1)**n. Its a bit unclear to me why exactly this is the case, but I’m going to trust it for now and improve on this editorial later. This seems to be an encoding problem.
rounds = 1
states: [dead, alive] (2**num_pigs)
rounds = 2
states: [dead_in_rd1, dead_in_rd2, alive] (3**num_pigs)
rounds = 3
states: [dead_in_rd1, dead_in_rd2, dead_in_rd3, alive] (4**num_pigs)
We are given minutesToDie and minutesToTest, so we can compute how many complete rounds we have for testing.
rounds = minutesToTest // minutesToDieNow its simply a matter of increasing the amount of pigs in the formula (rounds+1)**pigs until the result is greater or equal to the number of buckets provided to test.
Implementation
def poor_pigs(minutesToTest, minutesToDie, buckets):
rounds = minutesToTest // minutesToDie
pigs = 0
while (rounds+1)**pigs < buckets:
pigs += 1
return pigs
#time: o(log(buckets))
#memory: o(1)Instead of the while loop, we can also solve mathematically.
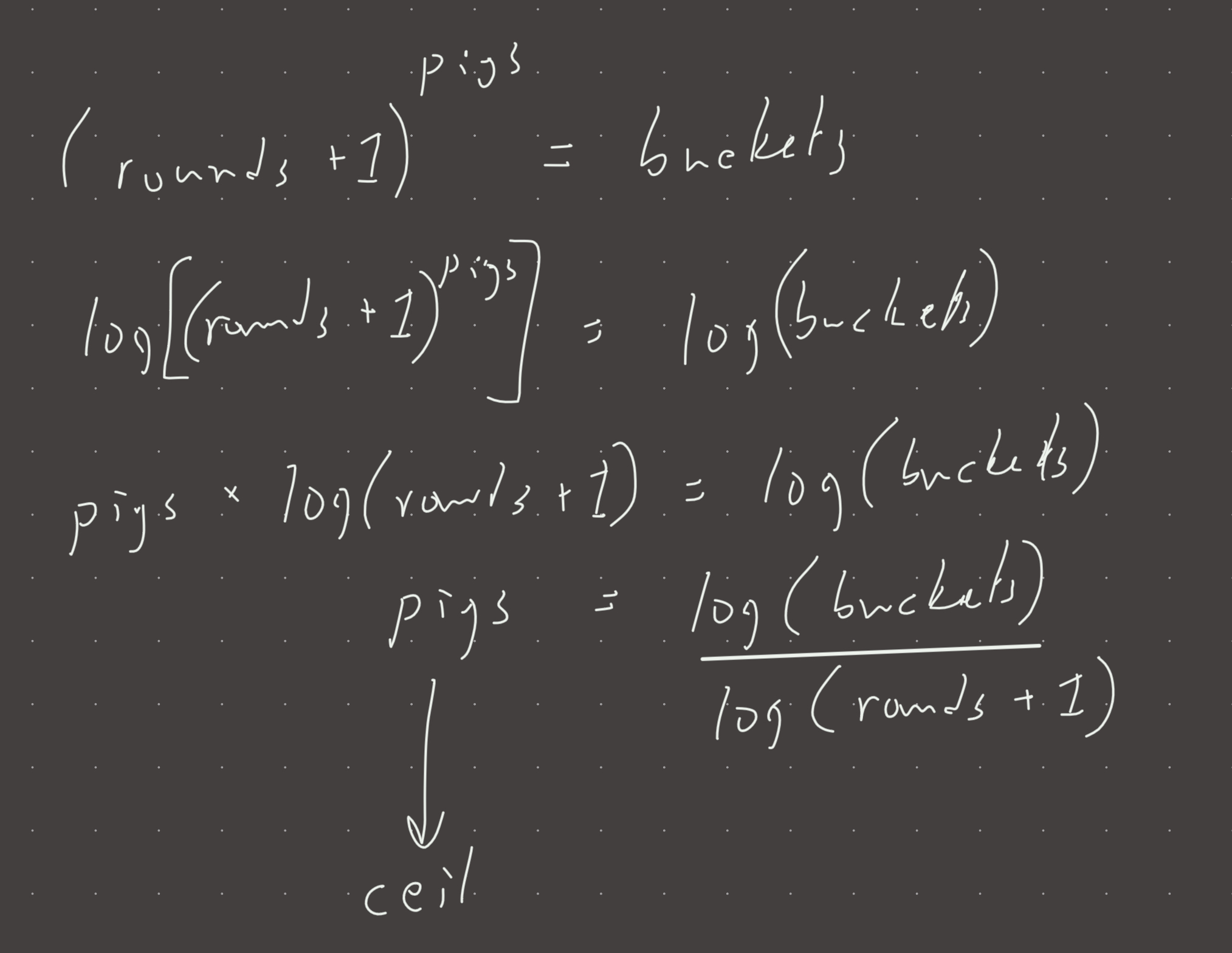
def poor_pigs(minutesToTest, minutesToDie, buckets):
rounds = minutesToTest // minutesToDie
return ceil(log2(buckets) / log2(rounds+1))
#time: o(1)
#memory: o(1)Visual
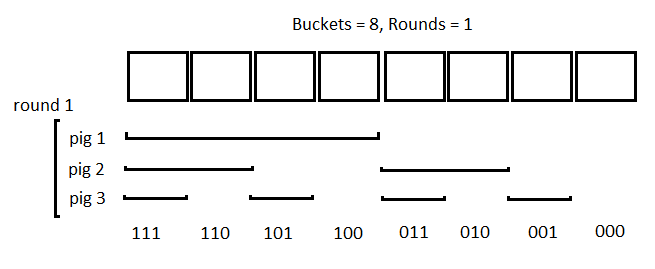
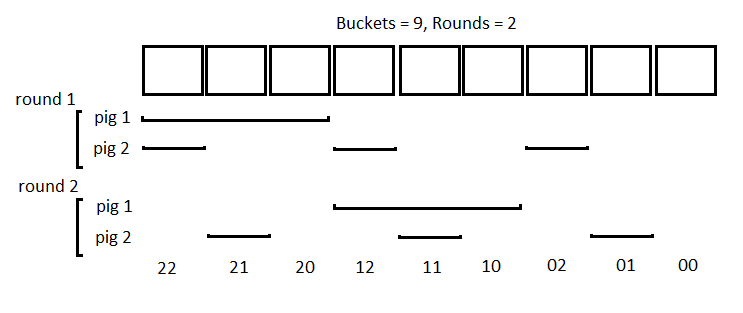
visuals from this solution https://leetcode.com/problems/poor-pigs/solutions/935172/two-diagrams-to-help-understanding/
Review 1
Just remember that 1 pig can test 2 buckets (lives or dies) in one round of testing…likewise 2 pigs can test 2**2 buckets…or 2**n more generally. So we keep increasing n until we reach or exceed buckets. If more tests are permitted (minutesToTest//minutesToDie) we increase the base.
Review 2
I understood that buckets are essentially the number of states, but it took a few minutes to realize what was the base and what was the exponent. The state of one pig is 2^1. Why? Because the base (2) represents the two possible states of a pig- dead or alive, and the exponent (1) is the number of pigs.
Basically, the possible states of a pig is number_of_tests+1 and the exponent is the number of pigs. So we just increase the value of pigs by 1 while (number_of_test+1)**pigs < buckets.
Cool problem.