Link: https://leetcode.com/problems/special-array-with-x-elements-greater-than-or-equal-x/
Solution:
DSA: sorted order, counting sort, suffix sum
Intuition
This is kind of and interesting problem. The constraints are so low that even a quadratic solution works fine, but the nlogn solution is pretty interesting. The key is to sort the numbers in ascending order, and see if the current element is greater or equal to the number of elements remaining. There are a few edge cases though when doing it this way.
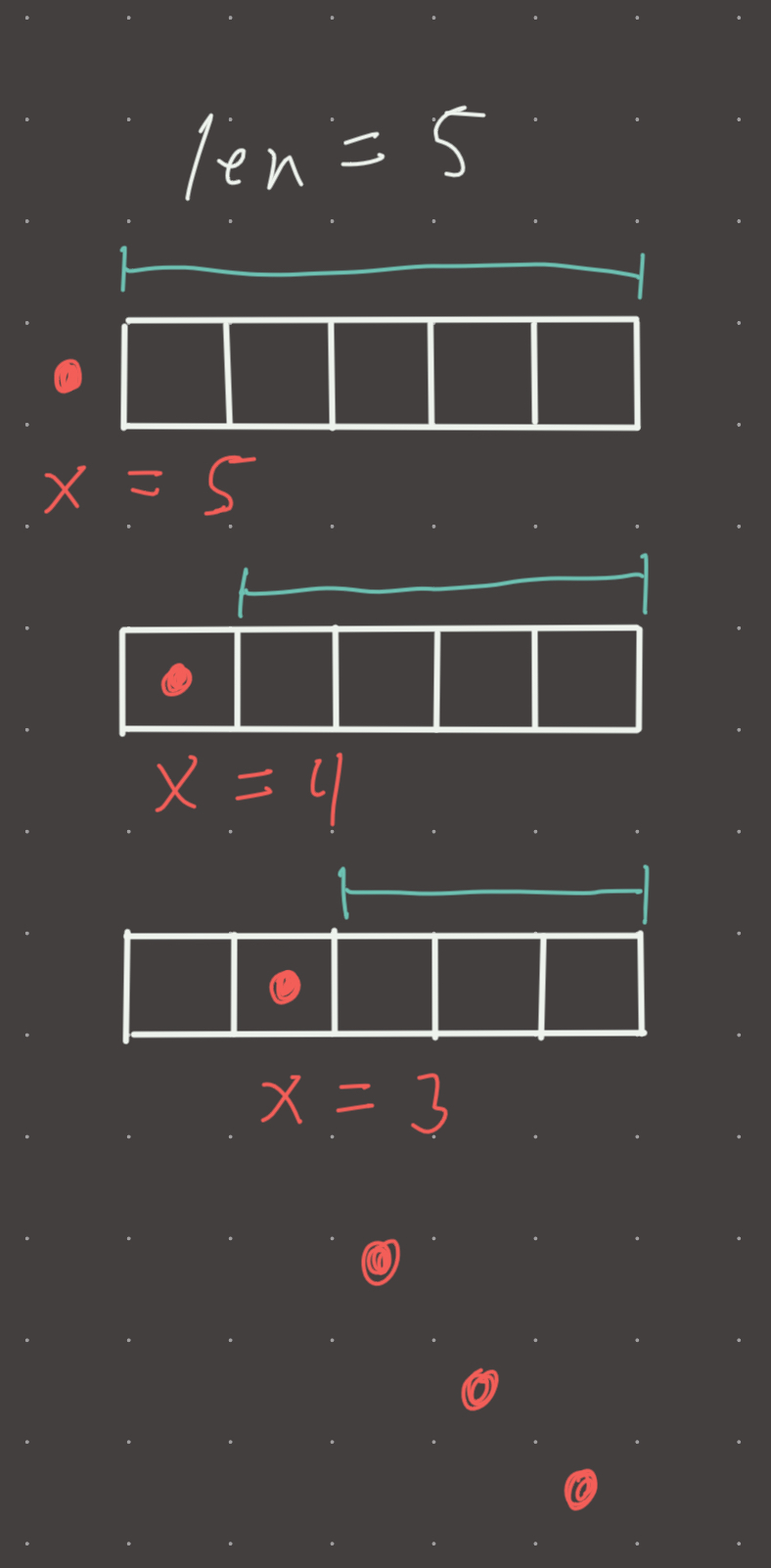
The key intuition is realizing that the answer x can only be between 0 and len(nums)! So after sorting, we can just iterate through nums and reduce the value of x . If the x <= nums[i] AND x > nums[i-1], we return x. Why the second part?
Consider the following example:
nums = [1, 2, 3, 4]
(x = 4, num = 1) x is not smaller or equal to num, keep going
(x = 3, num = 2) x is not smaller or equal to num, keep going
(x = 2, num = 3) x is not smaller than num so this 2 is the result...or is it?
Its not. If 2 is the answer that means there are exactly two numbers greater than or equal to 2. This is not the case here, as we have 3 numbers >= 2...
[2, 3, 4]
So what this means is that we must also make sure that x is GREATER than the the previous number, otherwise we could under count.
Implementation
def spec_array(nums):
nums.sort()
for i in range(len(nums)):
x = len(nums)-i
if nums[i] >= x and (i == 0 or nums[i-1] < x): #edge case for i = 0
return x
return -1Visual
Review 1
Interesting problem. I found the binary search solution almost instantly, and then did the counting sort / prefix sum solution…cool technique.
Implementation (counting sort + prefix sum)
def special(nums):
counts = [0]*1001
for num in nums:
counts[num] += 1
curr = 0
for i in range(len(counts)-1, -1, -1):
curr += counts[i]
if curr == i:
return i
return -1