Link: https://leetcode.com/problems/two-sum-ii-input-array-is-sorted/
Solution:
Topics: two pointer, two sum, sorted order
Intuition
A classic two pointer problem, only works on a sorted array. The key idea is to initialize two pointers at the start and end of the array. Then we intelligently move the pointers until we either reach a result or exhaust the array…the implementation is somewhat similar to binary search.
Moving left or right in a two pointer algorithm is decided by a condition. In this case, if the result of numbers[l] + numbers[r] is less than the target, we shift the left pointer…if the result is greater than the target, we shift the right pointer.
Compared to two sum, we can solve this problem in constant space. Note that while constant space is an advantage here, this also make the two pointer algorithm far less general than the the hash map needs pattern. two pointer can only be used if there exists an unambiguous condition by which to move the pointers. This makes the algorithm kind of niche…if you think about it though it kind of makes sense. The needs hash map pattern uses ALOT more resources, and from an information theory perspective the difference is quadratic even though hash maps have o(1) reads.
Implementation
def two_sum2(numbers, target):
l = 0
r = len(numbers)-1
while l < r:
total = numbers[l] + numbers[r]
if total == target:
return [l+1, r+1]
elif total > target:
r -= 1
else:
l += 1
#time: o(n)
#memory: o(1)Mnemonic
There is a very strange mountain. The mountain is strange because the slope is increasing, but with no consistency. You are standing at the bottom and your partner is at the peak. We are not allowed to move incrementally along a segment of slope, we can only jump from segment to segment (lets say you land in the middle). Your task is to find two segments on the mountain for yourself and your partner where the slope of a laser between the two of you is exactly target. There is guaranteed to be an answer.
Visual
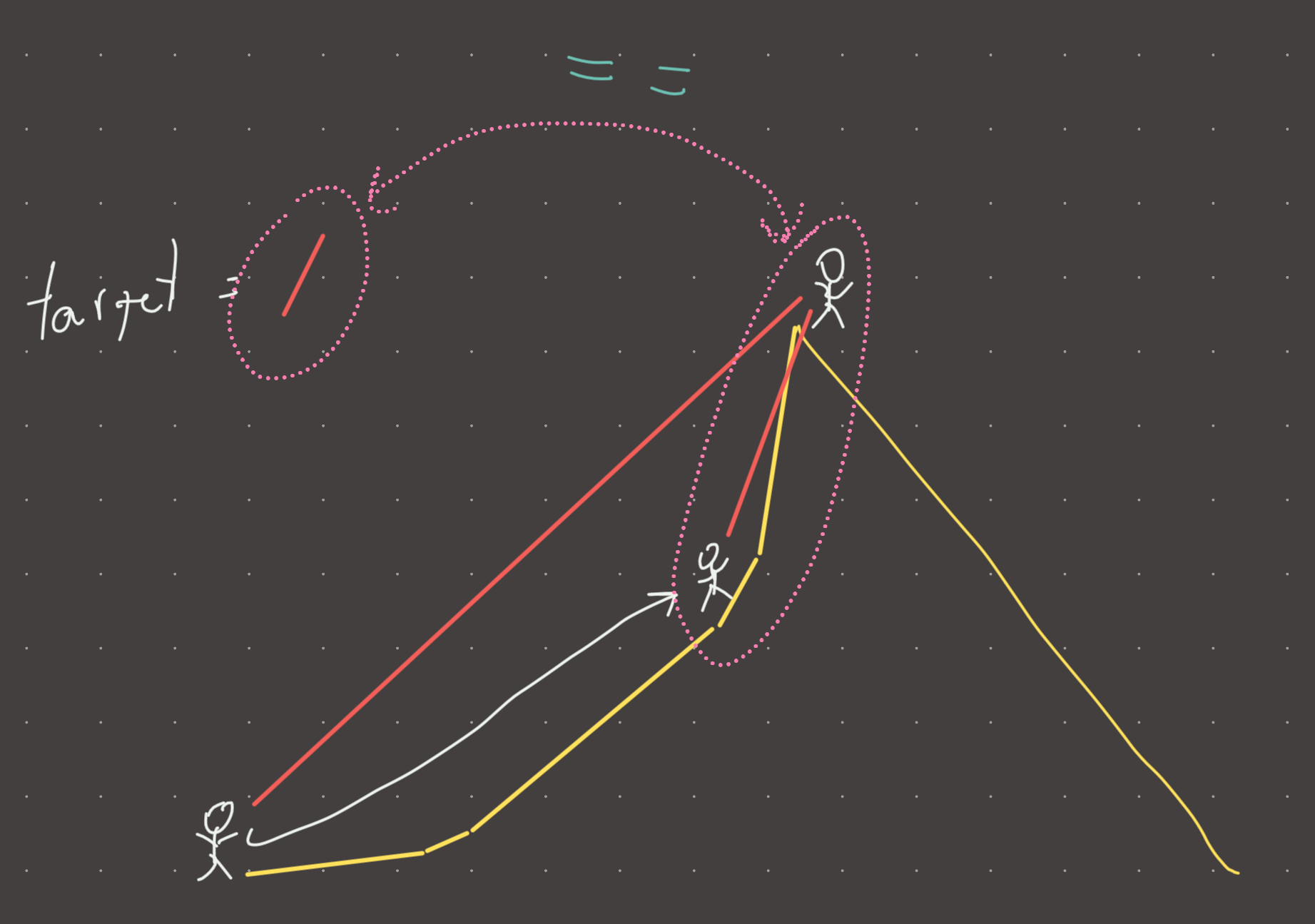
Review 1
Same as 3sum but the constraints are much more lax and there are only 2 pointers instead of 3.