Link: https://leetcode.com/problems/zigzag-conversion/
Solution:
Intuition
This is a pretty simple problem, but my initial solution was somewhat sub-optimal. Basically, I created a 2d array of size len(s)*numrows and did an overly complicated zigzag traversal by moving around two pointers.
It later occurred to me that we can just initialize an array of length numrows with empty strings, and then just go back and forth between them all the while appending the current character of s to the currently active index of our string array. We can keep the active index in a pointer and simply increment it when its < len(s)-1 and decrement its >= 0.
Implementation
def zigzag(s, numRows):
zigz = ['' for _ in range(numRows)]
index = 0
direction = 1
for char in s:
zigz[index] += char
if index == 0:
direction = 1
if index == numRows-1:
direction = -1
index += direction
return ''.join(zigz)
#time: o(n)
#memory: o(n)Mnemonic
Laser shooting targets in a periodic motion.
Visual
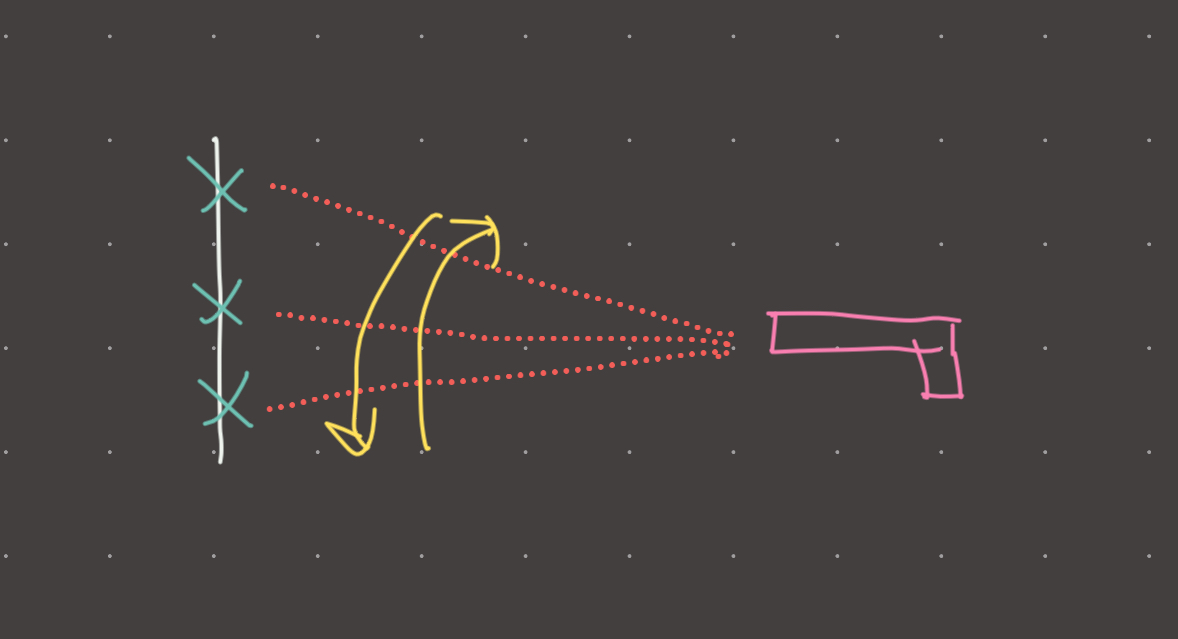
Review 1
Easy, removing the hard tag. I think a better approach than above is to set up a base case for if numRows == 1, in which case return s. This eliminates some edge cases.